Meloplasty SURGERY
Meloplasty and Platysmaplasty surgery procedures are established surgical options for individuals looking to address age-related changes in the face and neck area.
This guide outlines the different types of Meloplasty and Platysmaplasty surgery procedures available at our clinic, offering detailed information on the benefits and suitability of each technique to help you make an informed decision.
Meloplasty Surgery
1. Deep Plane Meloplasty
The deep plane Meloplasty is a surgical technique that targets the deeper layers of the face, including muscles and connective tissues. This approach allows for repositioning and tightening of facial structures beyond the skin, providing more substantial and longer-lasting results compared to traditional meloplasty.
Incision Placement: Incisions are typically made along the hairline and around the ears, similar to traditional facelifts, but extend deeper to access the underlying tissues.
Muscle Repositioning: The deeper facial muscles and tissues are lifted and secured to improve facial structure and support.
Mid-Facial Improvement: This technique is effective in addressing changes in the mid-face and cheek area by repositioning tissues to restore fullness and support.
2. Mid-Meloplasty
The mid-Meloplasty focuses on the central area of the face, specifically the cheeks and nasolabial folds. This procedure is suitable for patients with reduced volume in the mid-face region. By repositioning underlying tissues, the mid-facelift can help improve the structure and support of the mid-face.
This technique is often combined with other facial procedures to address multiple areas and achieve more comprehensive outcomes.
3. Platysmaplasty
As part of the aging process, the neck may develop excess skin and muscle banding. Platysmaplasty, addresses these changes. Cervicoplasty involves removing excess skin, while platysmaplasty tightens the neck muscles to improve the neck’s structure and support.
4. Temporal Brow Surgery
The temporal brow surgery is sometimes performed together with a deep plane meloplasty or platysmaplasty. This procedure helps to manage the skin and tissues around the outer corners of the eyes, supporting better alignment of the skin following surgery.
5. Fat Grafting (Fat Transfer)
Fat grafting involves removing fat from one part of the body and injecting it into areas of the face where volume has decreased or hollowness is present. This procedure uses your own tissue and can provide lasting results by restoring fullness to targeted areas.
6. Chin Implant
Chin implant is sometimes performed with a deep plane facelift/neck lift to augment the chin if it is recessed (small or set back).
What to Expect After Surgery
Drains
Drains are thin, flexible tubes placed during surgery to help remove excess fluid and blood from the surgical area. They assist the healing process and reduce the risk of complications such as hematomas (blood accumulation) or seromas (clear fluid accumulation) under the skin. Drains are typically removed the day after surgery.
Bandages
Bandages protect incision sites, help reduce swelling, and support the repositioned tissues after facelift surgery. These are usually removed alongside the drains on the first day after surgery.
Compression Garments
In some cases, patients may be advised to wear a compression garment around the head and neck. This applies gentle pressure to help reduce swelling and support healing. Compression garments are usually worn full-time for two weeks, then part-time for an additional two weeks.
Potential Risks – Meloplasty Surgery
As with any surgical procedure, a Meloplasty carries general and procedure-specific risks, including:
- Infection at the surgical site, which may require antibiotics or additional treatment
- Bleeding or haematoma (collection of blood under the skin)
- Scarring, which may be visible behind the ears or under the chin, depending on incision placement
- Nerve injury, which can lead to temporary or, rarely, permanent changes in sensation or facial movement (e.g. lower lip weakness)
- Changes in skin sensation, including numbness or tingling in the neck or earlobe areas
- Asymmetry or irregular contours following healing
- Persistent swelling or bruising, which may take several weeks to resolve
- Skin discolouration or irregular pigmentation in treated areas
- Delayed wound healing, especially in individuals who smoke or have other risk factors
- Skin or fat necrosis, although uncommon, may occur in areas with reduced blood supply
- Hair loss near incision sites, particularly around the hairline or behind the ears
- Anaesthesia-related risks, including allergic reactions or complications related to sedation or general anaesthetic
Recovery and Aftercare – Meloplasty Surgery
- Swelling, bruising, and tightness in the neck and jawline area are common and generally subside over several weeks
- Pain or discomfort is usually mild to moderate and can be managed with prescribed or over-the-counter pain relief
- Dressings and sometimes a compression bandage may be applied to support healing and minimise swelling
- Head elevation (including when sleeping) is usually recommended to reduce swelling and tension
- Cold packs may be used cautiously in the early stages to reduce swelling (as advised by your surgeon)
- Strenuous activity, bending, lifting, and exercise should be avoided for at least 3–4 weeks, or as directed by your surgeon
- Driving should only be resumed when you can move your neck comfortably and are no longer taking strong pain medications
- Incision care and scar management instructions will be provided and should be followed closely
- Smoking and alcohol should be avoided during recovery, as they can impair healing and affect results
- Final results may take months to fully appear, as residual swelling resolves and tissues settle
- Follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing and assess your outcomes
If you have any questions or wish to discuss Meloplasty options, please contact our clinic to schedule a consultation with Dr Reema Hadi.
If you would like more information on Meloplasty, you can visit the Australian Society of Plastic Surgery
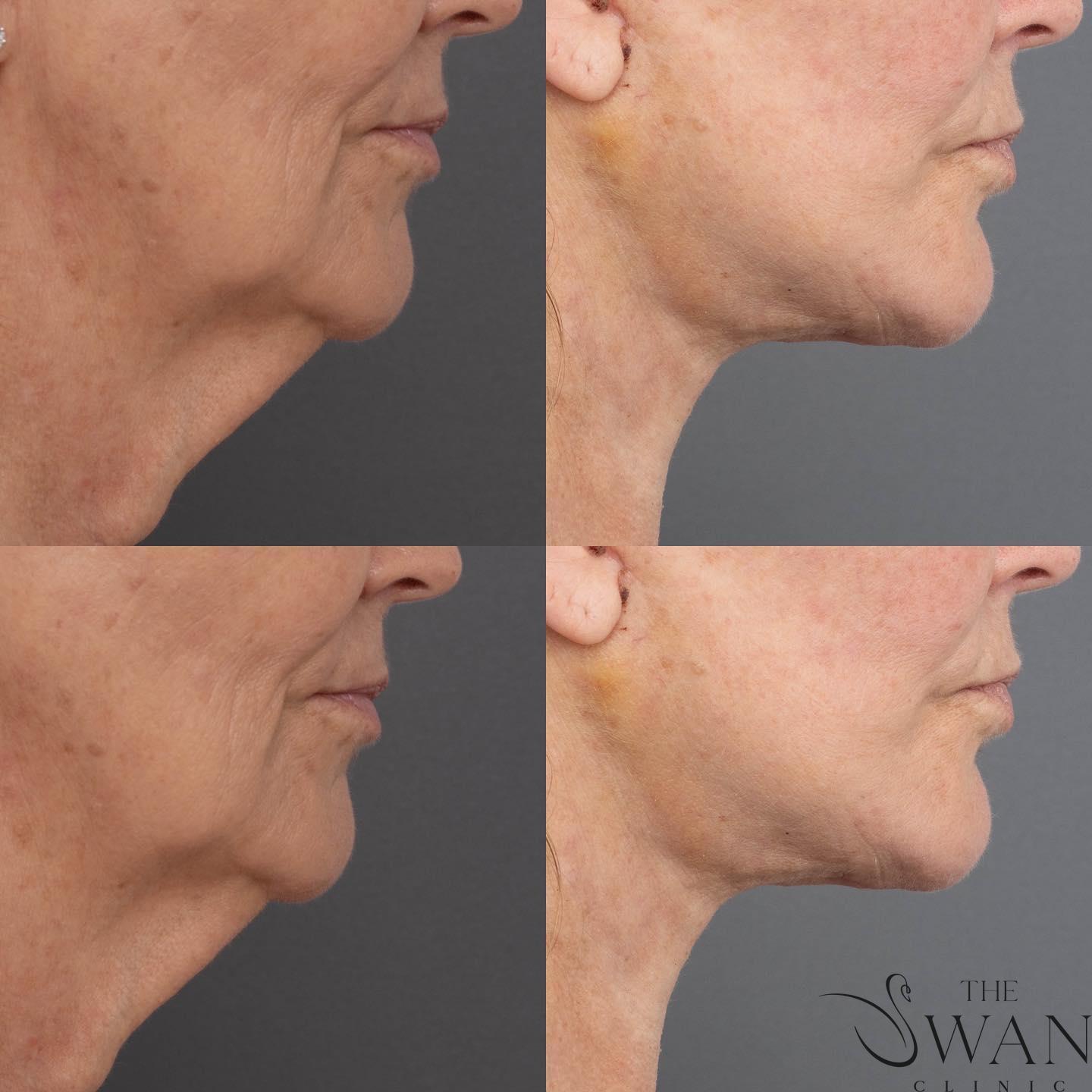
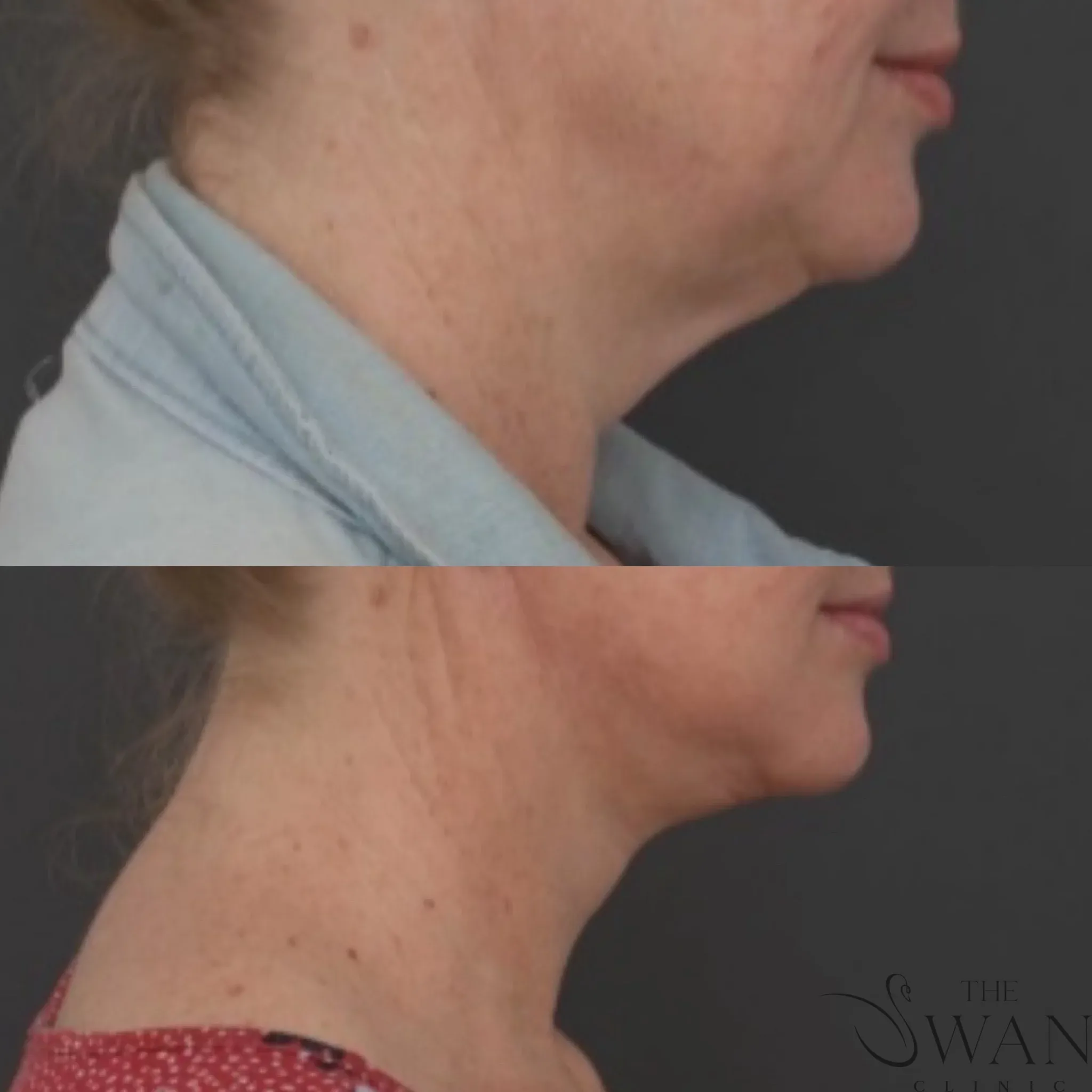
Before and After Photos
Real patient results from our expert procedures