Reduction Mammoplasty
Reduction mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of breast tissue, skin, and fat to reduce breast size. It may be considered by individuals experiencing physical symptoms such as neck or back discomfort, or difficulty with physical activity, which may be associated with larger breast size. The procedure also involves repositioning the nipple and reshaping the remaining tissue to suit the individual's body proportions. The specific approach and outcomes vary based on each patient’s anatomy and clinical needs.
Potential Benefits of Reduction mammoplasty
- Symptom Relief: Some individuals report reduced discomfort in areas such as the back, shoulders, or neck following breast reduction surgery.
- Movement and Activity: Some people find that reduced breast volume allows for greater ease during physical activity.
The Surgical Process
Before undergoing the procedure, a consultation is conducted to assess suitability, medical history, and individual goals. The surgeon will outline the procedure, explain potential risks, and discuss expected outcomes.
During surgery, excess breast tissue, fat, and skin are removed. The remaining tissue is then reshaped and repositioned. Incisions and techniques vary depending on the patient’s presentation and surgical plan. Scarring is expected, and the surgical team will discuss scar care and follow-up during the recovery process.
Pedicle Types in Reduction mammoplasty Surgery
In reduction mammoplasty surgery, the pedicle refers to the breast tissue segment that remains attached to its blood supply and nerves during the procedure. The choice of pedicle type depends on factors such as breast size, shape, degree of sagging (ptosis), and surgical considerations. Common pedicle types include:
- Inferior Pedicle: The pedicle is located at the lower part of the breast. This technique helps preserve blood supply and sensation while allowing reshaping and lifting. It is often used for patients with moderate to severe breast ptosis.
- Superior Pedicle: This pedicle is positioned at the upper portion of the breast. It is generally used for patients with less severe ptosis. The technique maintains blood supply and sensation and aims to reduce volume while providing some lift.
- Free Nipple Graft: This method is less commonly used and reserved for cases with very large reductions or significant ptosis. It involves detaching the nipple-areola complex and grafting it to a new position. This approach may lead to partial or complete loss of nipple sensation.
Incision Types in Reduction mammoplasty Surgery
The incision pattern is chosen based on breast size, skin quality, and the amount of tissue to be removed. Common incision types include:
- Anchor Incision (Inverted-T or Wise Pattern): Consists of three parts — around the areola, vertically from the areola to the breast crease, and horizontally along the breast crease. This approach allows for effective tissue removal and repositioning but may result in more visible scarring.
- Vertical Incision: Comprises an incision around the areola and a vertical incision down to the breast crease. Suitable for moderate ptosis and results in fewer scars compared to the anchor incision.
- Peri areolar Incision: A circular incision around the areola, typically used for mild ptosis with minimal scarring that blends with the areola border.
Choosing the Appropriate Technique
The selection of pedicle and incision type is tailored to each individual’s anatomy and surgical goals. During consultation, the surgeon will evaluate breast size, shape, ptosis severity, and skin quality to recommend an approach that aims to balance tissue preservation, sensation, and scarring.
Estimating Breast Size in Reduction mammoplasty Surgery
Estimating breast size is an important part of the pre-operative assessment in breast reduction surgery. Several methods are used to assist in planning the procedure and discussing realistic outcomes:
Key Techniques for Estimation
- Physical Examination: A detailed assessment of the breasts and chest is performed, evaluating volume, shape, symmetry, and skin quality.
- Breast Measurements: Measurements assist in assessing symmetry and determining the extent of tissue reduction. Common measurements include:
- Breast base width
- Nipple-to-inframammary fold distance
- Nipple-to-sternal notch distance
- Breast projection
- Breast base width
- 3D Imaging Technology: Some practices use 3D imaging to visualize breast volume and contours, which can help in surgical planning and provide patients with a visual understanding of potential changes.
- Cup Size Estimation: Existing bra cup size is considered as a reference, but the goal is to achieve a breast size and shape that is proportionate and suitable to the individual's body and preferences.
- Patient Input: Patient goals, lifestyle, and preferences are central to the decision-making process.
- Sample Photos: Patients may share images representing their desired outcomes, but results will be tailored to each individual’s unique anatomy.
By combining these approaches, the surgical plan can be customized to best meet each patient’s needs and expectations.
Potential Risks – Reduction mammoplasty Surgery
As with any surgical procedure, reduction mammoplasty carries risks, including general surgical risks as well as those specific to breast reduction:
- Infection at the surgical site, which may require antibiotics or further treatment
- Bleeding or haematoma (collection of blood under the skin)
- Changes in breast shape, size, or symmetry following surgery
- Scarring, which can be significant depending on incision type and individual healing
- Altered sensation in the breast or nipple area, which may be temporary or permanent
- Nipple or skin necrosis (rare), where tissue may lose blood supply
- Asymmetry or unevenness in breast appearance after healing
- Persistent pain or discomfort beyond the expected recovery period
- Seroma formation (fluid accumulation), which may require drainage
- Anaesthesia-related risks, including allergic reaction or respiratory complications
Recovery and Aftercare – Reduction mammoplasty Surgery
- Swelling, bruising, and mild to moderate discomfort are common and usually improve over several weeks
- Pain relief may be prescribed or managed with over-the-counter medication as directed by your surgeon
- Dressings and wound care instructions should be followed carefully to support healing and reduce infection risk
- Supportive bras or garments are typically recommended for several weeks to support the breasts and minimise swelling
- Strenuous activity, heavy lifting, and upper body exercise should generally be avoided for 4–6 weeks, or as advised by your surgeon
- Driving can usually be resumed once you are off prescription pain medication and feel physically able to do so safely
- Incision scars will fade over time but may remain visible; scar care options may be discussed with your surgeon
- Follow-up appointments are important to monitor healing, assess results, and address any concerns
- Smoking and alcohol should be avoided during recovery, as they may impair wound healing
- Final results may take several months to become apparent as swelling subsides, and tissues settle
If you would like more information on Reduction Mammoplasty, you can visit the Australian Society of Plastic Surgery
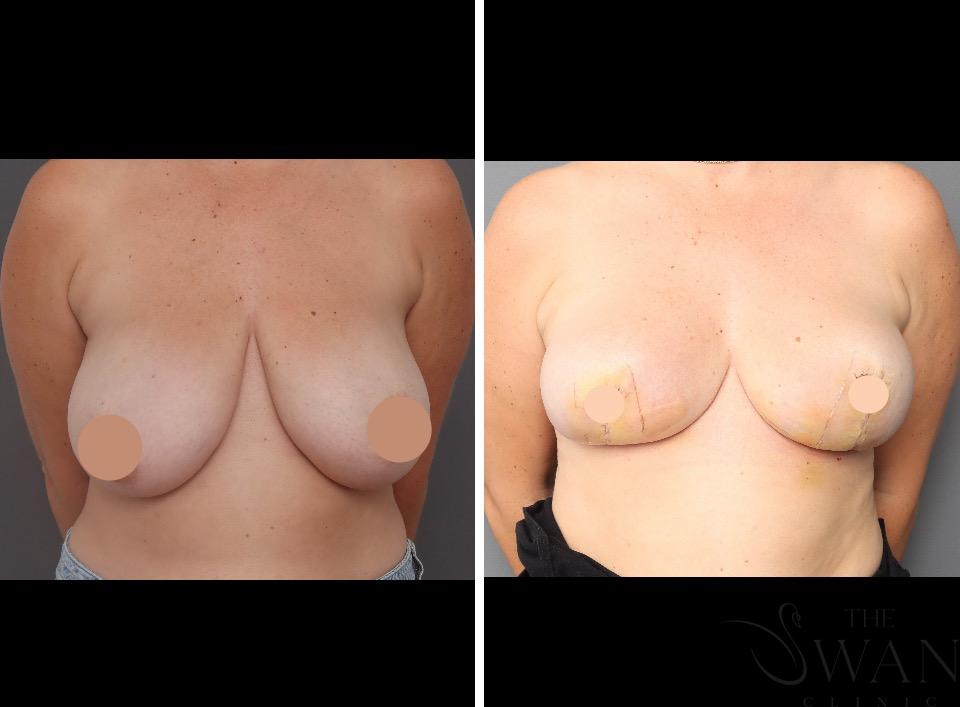
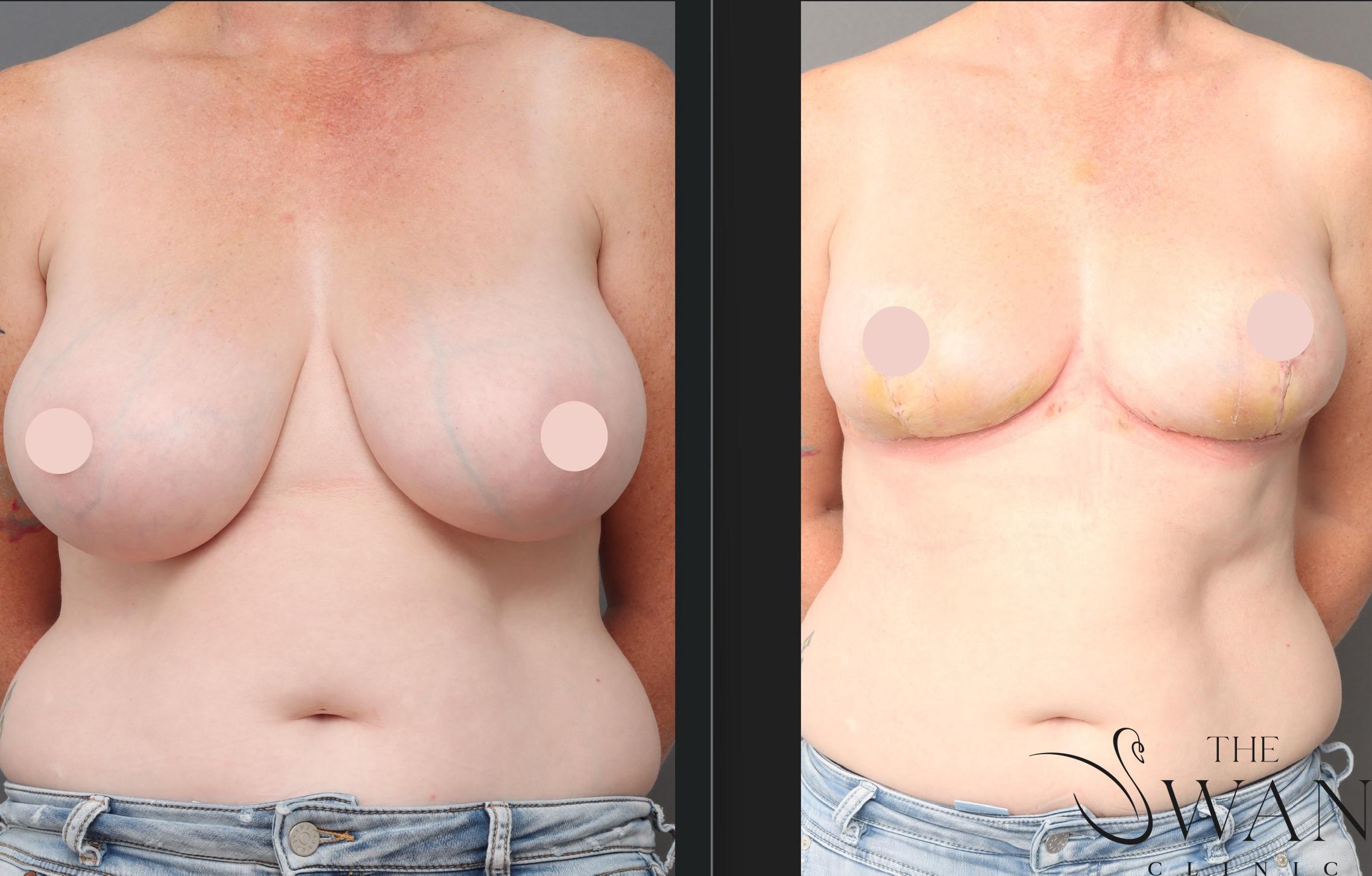
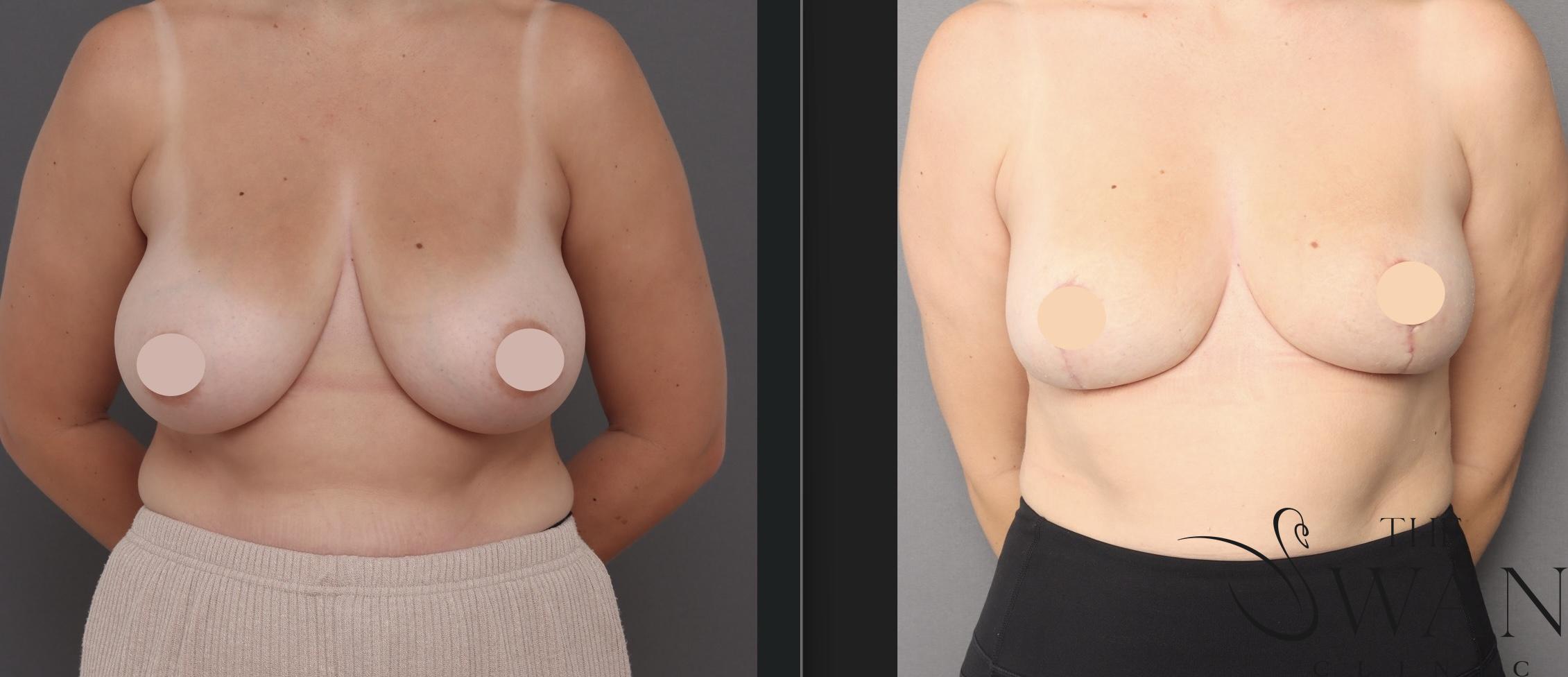
Before and After Photos
Real patient results from our expert procedures